Are you looking to get started with Linux Deploy? Are you curious about how to install, configure, and manage your Linux system? If so, you’ve come to the right place!
In this article, we’ll walk you through every step of the process, from setting up your deployment environment to deploying and managing your Linux system. With our easy-to-follow guide, you’ll be ready to deploy Linux in no time.
What is Kali Linux?
The Debian-based Kali Linux distribution was initially known as Backtrack. It is a vulnerable penetration-testing distribution with security auditing capabilities. Additionally, Kali Linux is a useful, accessible solution for professionals and hobbyists in information security.
Kali is a widespread Linux distribution based on Debian. Its goal is to include as many penetration and security audit tools as bundled in a complete package. Compared to other distributions, Kali has the most open-source tools compiled and prepared to use.
This distro is made for ethical hacking. It has all the tools you need to crack databases, access wireless networks, compromise security, and hack machines. That’s why most hackers use Linux on their laptops, on their live USBs, and on their windows computers.
Understanding Linux Deploy Security Features
When it comes to deploying Linux systems, security is one of the most important considerations to keep in mind. It’s important to protect your data and systems against malicious attacks, and one way to do that is by understanding the security features available in Linux deployments. By learning about these features, you can ensure that your Linux systems are secure and safe from harm.
Linux security features can be divided into two categories: those that are built into the operating system and those that are added on top. The most basic security features are built into the Linux kernel, the heart of the operating system. These features include access control lists, which give users the ability to determine who can access what files or processes; and file system access control, which prevents users from accessing unauthorized files or processes.
In addition to these built-in security features, many Linux distributions include additional security features that can be added or configured to further protect your system. These include firewalls, which can be used to block malicious traffic; intrusion detection systems, which detect and respond to attacks; and application whitelisting, which prevents unauthorized applications from running on the system.
When it comes to deploying Linux systems, it’s important to understand the security features available and how they work. By understanding these features and how they can be used to protect your systems, you can make sure that your system is secure and protected from malicious attacks.
How To Install Kali Linux On Android?
On the off chance that your present adaptation of Android doesn’t permit to effortlessly pick up root, consider looking at LineageOS and introducing that. Its a total trade for your present rendition of Android in view of open source advances. You should get proper Linux deploy repository to install kali Linux on your device.
A justifiable reason motivation to consider utilizing Lineage is this: some gadget makers bolt up the variant of Android they ship and make it almost difficult to pick up root get to. If so, the best game-plan is to supplant this adaptation with something unique. Ancestry OS has worked in the root, and backings a wide range of Android gadgets.
Required Apps
Download All The Required Apps For Further Processing.
BusyBox
Linux Deploy places a completely useful Linux working framework inside Android. It is a result of this, the application itself requires some Linux-perfect apparatuses. Fundamentally, the BusyBox toolbox.
There are numerous applications that can help clients on Android get BusyBox working, however by a long shot the most solid out there is this application here. Download it to your Android gadget, and open the application and install it. Then let’s move to the next step.
VNC Viewer
The exact opposite thing clients need to introduce before utilizing Linux send is a VNC watcher. This is on the grounds that however Linux Deploy introduces a whole working framework inside Android, it doesn’t really enable the client to straightforwardly get to it. This is a direct result of how Android is constructed.
A pleasant workaround is to introduce a VNC watcher application, to get to the graphical interface for your Linux introduce. There is a wide range of VNC watchers for Android, so don’t hesitate to introduce whichever one you’d like. In the instructional exercise, we’ll be utilizing a VNC Viewer.
Deploying Linux With Linux Deploy
At the point when every one of the prerequisites has been met (picking up root get to, introducing BusyBox, and introducing a VNC watcher) the Linux establishment can start. Begin off by downloading the Linux Deploy application to your gadget.
At the point when the application is introduced, open it. Tap the three speck symbol at the upper right. Look down and empower “VNC”. Also, search for the default username and secret key. Linux Deploy naturally creates one. Record them, at that point make a beeline for the primary screen.
Out of the container, Linux convey will set up a Debian Linux condition. This is adequate for general clients. In the event that you totally need to transform it into something unique, head into the settings.
To begin the establishment procedure, tap the “begin” catch. From here, the application will assume control. It’ll experience and assemble a Debian Linux introduces straightforwardly on your Android telephone or tablet! Sit back, read the prompt and pause!
Accessing The Linux Installation
Linux is installed. Presently it’s a great opportunity to really utilize it. To do this, open Linux conveys and tap the play catch (if it’s not effectively running). Open the VNC application, at that point tap the green in addition to the symbol to make another association. In the association director, there are two fields: Address and Name.
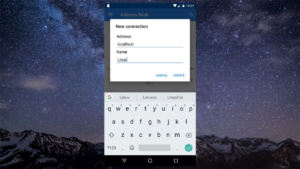
Under “Address”, type “localhost”. In the name area, type whatever you’d get a kick out of the chance to call the association. Rounding out the data makes another association, and raises an association screen. At the base of the screen, tap the enormous “associate” catch.
From here, the VNC apparatus will provoke for the secret word. Enter the watchword you recorded before to access your Linux establishment. So, this is all about Linux deploy tutorial. Feel free to contact us if you face any issues or problems.
How To Troubleshoot common issues with installing Linux Deploy
Troubleshooting common issues with Linux Deploy can be a daunting task, especially for those just starting out with Linux. However, with a bit of patience and understanding, you can successfully troubleshoot and resolve various issues that can arise while deploying and managing Linux. In this blog post, we’ll discuss some of the common issues experienced when deploying Linux, such as network connection issues, permissions issues, and app installation issues.
Network Connection Issues
Network connection issues are among the most common issues faced when deploying Linux. Connectivity issues can occur due to a number of reasons, including incorrect IP address settings, DNS misconfigurations, or hardware incompatibilities. To troubleshoot network connection issues, try these steps:
First, make sure that the network cable is securely connected to the network adapter.
Check if the IP address settings are set correctly, and if necessary, reset them.
Check if the DNS settings are set correctly.
Check if the network adapter drivers are up-to-date, and if necessary, install the correct drivers.
Permissions Issues
Permissions issues can also arise when deploying Linux, and can prevent you from accessing certain resources or running certain applications. To resolve permissions issues, try these steps:
Check if the user has the correct permissions for the resource or application in question.
If necessary, change the permissions for the user or group in question.
Check if the user or group has sufficient privileges to perform the required task.
App Installation Issues
App installation issues are also common when deploying Linux, which can be resolved by taking the following steps:
Check if the installation package is compatible with the Linux version being used.
If necessary, download the correct version of the installation package.
Check if the user has the correct permissions to install the application.
Check if the user has sufficient disk space to install the application.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Linux Deploy is a powerful tool that allows users to easily deploy and manage Linux systems. It offers a wide variety of features and benefits, including faster deployment, ease of use, and the potential for greater scalability. By following the tips for getting started with Linux Deploy, users can quickly and easily set up their own Linux system. This can help to save time, money, and resources, making it a valuable tool for any user.












